
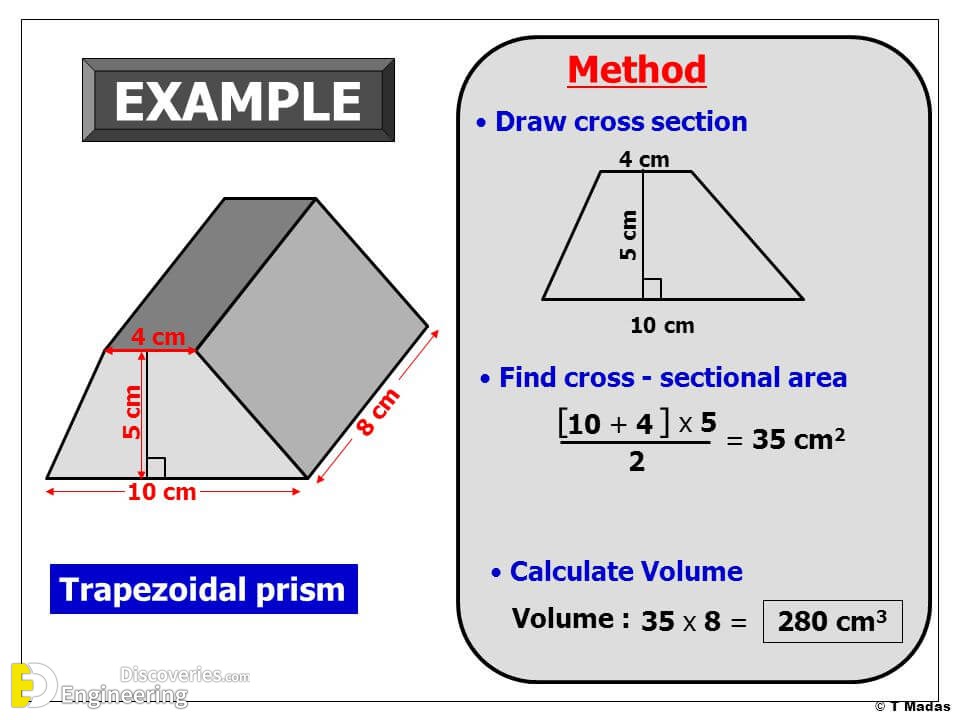
There are 4 standard types of interstitial sites, categorized by the number of surrounding atoms. However, near the end of this article I will explain how martensite arises from the difference in interstitial size between FCC and BCC iron.
#Crystalmaker calculate volume how to#
The strongest phase of steel, martensite, exists because of carbon’s interaction with iron’s interstitial sites.įor now, I should explain more about how to perform calculations with interstitial sites. If you know anything about metallurgy, you should know that steel is one of the most important materials in the world–mostly because of the way metallurgists can make its phases interact. The most famous example of an interstitial solid solution is when carbon rests in interstitial sites of iron–this is steel. There are entire alloys based on this principle, called interstitial solid solution alloys. Usually, this strains the crystal lattice and increases the strength of a metal. Interstitial defects usually happen when a small atom fills the interstitial site of a larger atom’s crystal structure.
There are many kinds of crystal defects (besides interstitial defects) such as grain boundaries, vacancies, and dislocations. When the interstitial site is not empty, it is considered an “interstitial defect.” Defects allow some of the most important material properties, such as ductility in metals. Depending on the number of atoms surrounding that empty space, the interstitial site can be designated as triangular (3), tetrahedral (4), octahedral (6), or cubic (8).Įach interstitial site is empty in a perfect crystal, but since these are the regions in the crystal with the most empty space, imperfect crystals have an occasional atom in these sites.
Interstitial sites are empty spaces in a crystal lattice. If you have any pattern which doesn’t fill space completely (and we model atoms as spheres that can never fill space completely), you end up with gaps.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
